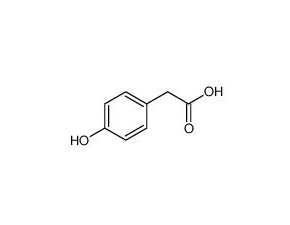
4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
CAS No. 156-38-7
4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M18084 CAS No. 156-38-7
4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid is considered to be slightly soluble (in water) and acidic. 4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid can be synthesized from acetic acid.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 52 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid is considered to be slightly soluble (in water) and acidic. 4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid can be synthesized from acetic acid.
-
Description4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid is considered to be slightly soluble (in water) and acidic. 4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid can be synthesized from acetic acid. It can be found throughout numerous foods such as Olives, Cocoa beans, Oats, and Mushrooms. 4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid can be found throughout all human tissues and in all biofluids. Within a cell, 4-Hydroxybenzeneacetate acid is primarily located in the cytoplasm and in the extracellular space.(In Vivo):4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (6, 12, or 25 mg/kg) increases Nrf2 translocation to the nucleus and enhances the activity of phase II and antioxidant enzymes. The protein levels of nuclear Nrf2 are increased by 170% and 230% in pre-treated 12 and 25 mg/kg 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid groups, respectively, compared with the control group.The 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid pretreatment at a final dose of 25 mg/kg markedly and selectively up-regulated the target genes of phase II enzymes and resulted in higher up-regulation than that of the control group by 270%, 400%, and 500% or UGT1A1, UGT1A9, and SULT2A1, respectively. 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid also suppresses the expression of CYP2E1.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (6, 12, or 25 mg/kg) increases Nrf2 translocation to the nucleus and enhances the activity of phase II and antioxidant enzymes. The protein levels of nuclear Nrf2 are increased by 170% and 230% in pre-treated 12 and 25 mg/kg 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid groups, respectively, compared with the control group.The 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid pretreatment at a final dose of 25 mg/kg markedly and selectively up-regulated the target genes of phase II enzymes and resulted in higher up-regulation than that of the control group by 270%, 400%, and 500% or UGT1A1, UGT1A9, and SULT2A1, respectively. 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid also suppresses the expression of CYP2E1.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number156-38-7
-
Formula Weight152.15
-
Molecular FormulaC8H8O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL; 657.25 mM
-
SMILESOC(=O)Cc1ccc(cc1)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
NPF
NPF
-
NO-711ME
NO-711ME is a prodrug of NO-711. It also is a potent and selective GABA uptake inhibitor.
-
Erythromycin A enol ...
Erythromycin A enol ether is a degradation product of Erythromycin A which is a macrolide antibiotic.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


